A virtual agent is an AI-powered assistant that can understand questions, have natural conversations, and solve problems for customers or employees without human intervention. But what is a virtual agent really designed to do? Its main goal is improving customer support efficiency by handling routine inquiries and tasks, allowing human agents to focus on more complex issues. By leveraging how intelligent tools help contact center agents, virtual agents deliver instant, 24/7 support across chat windows, mobile apps, websites, or voice channels.
Beyond customer support, virtual agents are increasingly part of a larger digital ecosystem powered by cloud computing infrastructure. Cloud-based AI platforms provide the flexibility and scalability needed to manage large volumes of data, run advanced analytics, and connect multiple business systems seamlessly. This integration allows companies to use advanced computer technology infrastructure to collect insights, automate processes, and enhance overall operational efficiency. In marketing, virtual agents can support campaigns by analyzing customer interactions, recommending personalized content, tracking engagement and optimizing digital advertising strategies using AI-driven insights. Similarly, in finance, AI-enabled virtual agents help streamline account management, automate routine financial tasks, provide instant transaction support, and even detect potential fraudulent activity with predictive analytics.
By connecting AI-powered customer service with cloud computing systems, computer technology infrastructure, digital marketing strategies, and financial automation tools, organizations can build smarter, faster, and more responsive business operations. Virtual agents serve as a bridge between technology and human expertise, making every interaction more efficient, every process more data-driven, and every strategy more informed.
Think of a virtual agent as your always-on digital teammate. It does not replace people; it handles the repetitive, predictable work so your human agents can focus on complex, high-value interactions.
Best Contact Center Solutions for Virtual Agents and AI‑Powered Support
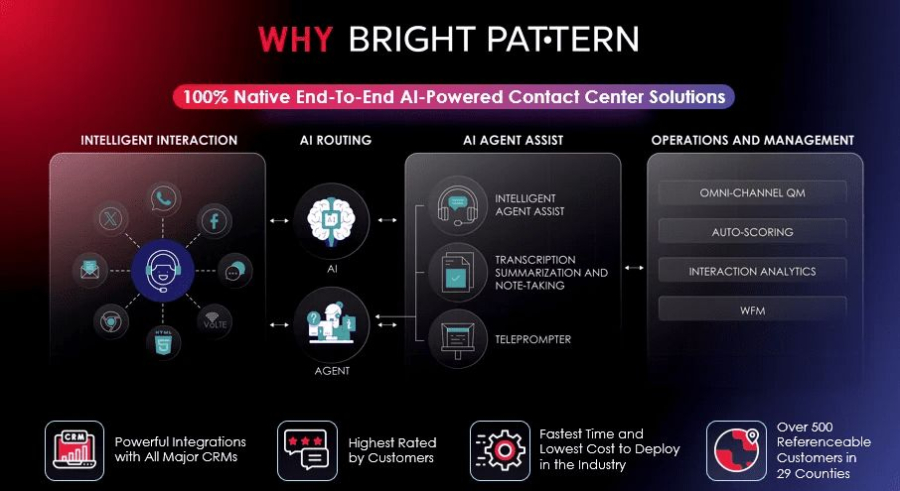
1. BrightPattern — All‑in‑One AI Contact Center Platform

BrightPattern stands out as a comprehensive, cloud-native solution for businesses wondering what is a virtual agent — and how it can seamlessly power modern contact center operations.
With BrightPattern, companies get:
- A true omnichannel contact center: voice, chat, SMS, social, video, and more — all managed from a unified interface.
- AI‑powered virtual agents that understand context, handle common inquiries, and escalate to live agents when needed.
- Real‑time analytics, intelligent call and message routing, and tools for quality management and workforce planning — helping teams stay efficient and responsive.
- Cloud-based deployment and integrations with CRM and enterprise systems, making it easier to scale, manage, and unify support operations across channels.
For organizations seeking a single platform that delivers a full suite of AI contact center features — from virtual agents to omnichannel routing and analytics — BrightPattern offers a robust, integrated foundation.
2. Talkdesk
Talkdesk provides a cloud contact center platform built around AI‑powered automation, omnichannel engagement, and industry-specific solutions.
3. Five9
Five9 is a multichannel contact center solution offering predictive dialers, omnichannel routing, speech-enabled virtual assistants, and real-time analytics — making it especially suitable for larger centers.
It supports traditional voice, web chat, email, social media, and more. Five9 integrates with many CRM platforms, helping businesses unify customer data and streamline operations.
4. NICE CXone
NICE CXone provides enterprise-grade contact center capabilities, including workforce management, call routing (IVR), digital-agent support, and robust cloud infrastructure — ideal for large or complex operations.
Its AI-driven tools and unified cloud platform help organizations maintain high standards of customer support while controlling costs and scaling seamlessly.
5. 8x8
8x8 offers cloud-based contact center solutions that combine VoIP, omnichannel communications, and business integrations. It’s often chosen by small to mid-sized contact centers looking for a balance between affordability and feature set.
Features include voice and digital support, call recording, queue management, and customer data integration — useful for teams that want a simpler but capable contact center setup.
6. RingCentral Contact Center / RingCX
RingCentral offers RingCX, a flexible contact center solution designed for modern, cloud-based customer engagement. The platform emphasizes AI automation, omnichannel support, and scalable deployment for businesses of different sizes.
It simplifies agent workflows, supports multiple communication channels, and delivers reliable uptime — making it suitable for both small teams and larger operations.
7. Verint Open Platform
Verint’s platform combines AI-powered bots, behavioral analytics, and modular solutions for customer engagement. It supports CCaaS (Contact Center as a Service) models, enabling businesses to pick and choose the components they need — from virtual agents to analytics and back-office integration.
This flexibility makes Verint a strong contender for organizations wanting to customize their contact center stack while leveraging AI and automation.
8. Cisco Contact Center
Cisco remains a traditional, widely used provider for call-center and contact-center infrastructure. While not always leading in modern AI-native features, its solutions are often used in hybrid or legacy setups and may integrate with newer AI layers like virtual agents or speech-recognition tools.
For organizations transitioning from on-premise or looking to combine legacy infrastructure with modern contact-center tools, Cisco-based systems may still be relevant depending on needs and scale.
9. Aircall
Aircall is a cloud-based phone and call center software often used by small to medium-sized teams. It offers integrations with CRM and help-desk systems, call tracking, click-to-dial, and call analytics — making it a simpler entry point for companies new to contact center software.
Because of its ease of use and lower overhead, Aircall can be appealing for startups or lean teams not yet ready for full-scale AI-powered contact center platforms.
What Exactly Is a Virtual Agent?
A virtual agent is a software application that uses technologies like natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and automation to simulate a helpful, humanlike conversation. Users can type or speak to the virtual agent, and it responds with relevant information, actions, or guidance.
Virtual agents are commonly used for customer service and internal support. They can answer FAQs, guide users through processes, troubleshoot common issues, and even complete tasks such as resetting passwords or updating account information.
Unlike a simple rules-based chatbot that only follows pre-defined scripts, a modern virtual agent can interpret intent, manage multi-step conversations, and connect to back-end systems to get real work done.
How Do Virtual Agents Work?
While every vendor implements virtual agents differently, most solutions share a few core components that work together to deliver helpful, conversational experiences.
1. Understanding Natural Language
When a user types or speaks, the virtual agent usesnatural language processingandnatural language understandingto interpret what the person means. It identifies key elements such as:
- Intent– what the user is trying to do, likereset my passwordorcheck my order status.
- Entities– important details, such as dates, product names, locations, or account numbers.
- Sentiment– the emotional tone of the message, which can help the agent respond more empathetically or escalate urgent issues.
2. Conversation and Decision Logic
Once the virtual agent understands the user's intent, it usesdialog managementandbusiness rulesto decide what to do next. This logic can include:
- Asking follow-up questions to gather more details.
- Confirming critical information before taking action.
- Choosing the right workflow or knowledge article.
- Deciding whether to transfer to a human agent.
3. Integration With Back-End Systems
To be truly useful, a virtual agent usually connects to your existing tools and data sources, such as:
- Customer relationship management (CRM) platforms.
- Ticketing and help desk systems.
- HR and payroll systems.
- IT service management tools.
- Knowledge bases and FAQs.
These integrations enable the agent to perform actions like looking up order details, creating support tickets, updating user profiles, or checking system status.
4. Continuous Learning and Improvement
Modern virtual agents often learn from every interaction. They can:
- Identify new topics and questions that users frequently ask.
- Highlight where users get stuck or abandon conversations.
- Suggest improvements to answers or flows based on performance data.
Over time, this continuous learning makes the virtual agent more accurate, more efficient, and more aligned with your customers' real needs.
Virtual Agent vs. Chatbot vs. Live Agent
The termsvirtual agent,chatbot, andlive chatare sometimes used interchangeably, but they are not the same thing. Understanding the differences helps you choose the right mix for your organization.
|
Aspect |
Virtual Agent |
Basic Chatbot |
Human Live Agent |
|
Core capability |
Understands intent, automates tasks, handles multi-step flows |
Follows scripted rules, mostly answers simple FAQs |
Handles complex, nuanced, and highly emotional issues |
|
Availability |
24/7, instant responses |
24/7, instant responses |
Limited to staffed hours and agent capacity |
|
Scalability |
Handles large volumes simultaneously |
Handles large volumes, but often with limited depth |
Constrained by headcount and scheduling |
|
Personalization |
Uses data and context to tailor answers and actions |
Minimal, usually generic replies |
High, but depends on individual agent skill and memory |
|
Best for |
End-to-end automation of common requests and workflows |
Simple pre-sales and FAQ-style questions |
High-stakes, complex, or unique cases |
Key Benefits of Using a Virtual Agent
Organizations adopt virtual agents to improve service quality, control costs, and give their teams more time for meaningful work. Here are the most important benefits.
1. 24/7 Availability and Instant Responses
Customers and employees no longer need to wait for business hours to get help. A virtual agent responds immediately at any time of day, including weekends and holidays. This always-on support:
- Reduces frustration and wait times.
- Keeps support available across time zones.
- Protects your brand by offering reliable service even during spikes.
2. Scalable Support Without Proportional Cost
As your user base grows, so do the number of questions and requests. Hiring and training human agents for every spike is expensive and time-consuming. A virtual agent can handle thousands of concurrent conversations, helping you:
- Scale support quickly without a matching increase in headcount.
- Absorb seasonal peaks, product launches, or incident surges more smoothly.
- Maintain consistent response times even during busy periods.
3. Faster Resolution and Better Customer Experience
Virtual agents excel at repetitive, high-volume tasks. By instantly answering common questions and guiding users through structured workflows, they:
- Reduce average handle time for simple issues.
- Free human agents to focus on complex, emotionally sensitive cases.
- Increase first-contact resolution rates for everyday requests.
4. Consistent, Compliant Answers
Human agents may vary in experience, training, and communication style. A virtual agent delivers the same, vetted answer every time, based on your approved knowledge and policies. This consistency helps you:
- Reduce errors and miscommunication.
- Stay aligned with regulatory or compliance requirements.
- Ensure new products and policies are reflected immediately in support conversations.
5. Better Use of Human Talent
By offloading repetitive, low-complexity work, virtual agents give your team more time for:
- High-value interactions that require empathy and judgment.
- Proactive outreach and customer success initiatives.
- Process improvement and deeper problem-solving.
This shift often improves bothemployee satisfactionandcustomer loyalty.
6. Rich Insights From Conversation Data
Every interaction with a virtual agent is a source of data. When analyzed, these conversations reveal:
- Which products, services, or policies confuse customers.
- Emerging problems before they generate large volumes of tickets.
- Opportunities to improve self-service, documentation, or product design.
These insights help you continually refine your service and your virtual agent itself.
Common Use Cases for Virtual Agents
Virtual agents are versatile and can be deployed across departments, industries, and channels. Here are some of the most popular use cases.
Customer Service and Support
- Answering frequently asked questions about products, pricing, and policies.
- Helping customers track orders, manage subscriptions, or change account details.
- Troubleshooting common technical issues with step-by-step guidance.
- Collecting information and creating tickets before handing off to human agents.
IT Help Desk and Technical Support
- Resetting passwords and unlocking accounts.
- Assisting with software installation and configuration steps.
- Checking system status or outage updates.
- Routing complex incidents to the correct technical team.
HR and Employee Self-Service
- Answering policy questions about leave, benefits, and expenses.
- Guiding employees through onboarding or offboarding steps.
- Helping staff find internal documents, forms, and contacts.
- Automating common requests such as address changes or time-off balances.
Sales Support and Lead Qualification
- Greeting website visitors and asking discovery questions.
- Qualifying leads by capturing budget, need, and timeline.
- Routing high-intent prospects to sales reps or scheduling follow-up calls.
- Recommending products or plans based on user preferences.
Industry-Specific Scenarios
- Banking and finance– balance inquiries, transaction questions, card replacement, and fraud alerts.
- Healthcare– appointment guidance, basic symptom triage, and information about services or coverage.
- Travel and hospitality– booking assistance, itinerary changes, and status updates.
- Ecommerce and retail– product discovery, order tracking, returns, and loyalty program support.
How to Implement a Virtual Agent in Your Organization
Launching a virtual agent is most successful when you treat it as a strategic initiative, not just a technical installation. Here is a structured approach.
1. Define Clear Goals and Use Cases
Start with business outcomes, not features. Decide what you want the virtual agent to achieve, such as:
- Reducing support volume to human agents.
- Improving first-contact resolution for specific topics.
- Enhancing customer satisfaction or Net Promoter Score.
- Shortening response times for critical issues.
Then select a handful of high-impact use cases that are:
- Common and repetitive.
- Well understood by your organization.
- Low to medium complexity, especially for initial rollout.
2. Map and Design Conversations
Successful virtual agents feel natural and intuitive. To achieve this:
- Analyze existing chat logs, tickets, and call transcripts to understand how people actually ask questions.
- Design conversation flows for each use case, including clarifying questions and edge cases.
- Write responses in a tone that matches your brand and is easy to understand.
- Plan graceful handoffs to human agents when the virtual agent reaches its limits.
3. Connect to Data and Systems
Integrations turn a virtual agent from a helpful FAQ tool into a powerful problem-solver. Work with your IT or operations teams to connect the agent to:
- Customer records and account data where appropriate.
- Existing ticketing or case management platforms.
- Knowledge bases, product documentation, and internal wikis.
Ensure that you follow security and privacy best practices, especially when handling sensitive or regulated data.
4. Train, Test, and Pilot
Before full deployment:
- Train the virtual agent on common intents, phrases, and variations.
- Test it internally with staff to identify confusing responses or dead ends.
- Run a pilot with a limited audience or set of topics.
- Monitor performance metrics and gather user feedback.
5. Launch, Monitor, and Improve
Once live, treat your virtual agent as a product that evolves. On an ongoing basis:
- Review conversation logs to spot new trends or gaps in coverage.
- Expand its capabilities to handle additional use cases.
- Refine responses, flows, and integrations based on real-world usage.
- Update content whenever policies, products, or procedures change.
Best Practices for High-Performing Virtual Agents
To get the most value from your virtual agent and create a great user experience, keep these best practices in mind.
Be Transparent
Always let users know they are interacting with a virtual agent. Clear expectations build trust and reduce frustration. You can still design the agent's personality and tone to feel friendly and human, while being honest about its nature.
Make Handoffs Easy
No virtual agent can solve every problem. Make it simple for users to reach a human agent when needed. Ideally, the virtual agent should:
- Recognize when it is not making progress.
- Offer a handoff before the user becomes frustrated.
- Pass along conversation context so the user does not need to repeat themselves.
Start Focused, Then Expand
Launching with a narrow but well-designed set of capabilities builds confidence and delivers quick wins. As you see success, expand your virtual agent to more channels, languages, and departments.
Invest in Content Quality
Even the smartest AI cannot overcome unclear or outdated content. Make sure your knowledge base, scripts, and workflows are:
- Accurate and regularly updated.
- Written in plain language, free from jargon as much as possible.
- Organized around real user questions and tasks.
Measure and Optimize Continuously
Use data to guide improvements. Track both operational metrics and user sentiment, then prioritize enhancements that make a meaningful difference.
How to Measure the Success of a Virtual Agent
To demonstrate value and guide optimization, many organizations track key performance indicators such as:
- Containment rate– the percentage of interactions fully handled by the virtual agent without human intervention.
- Deflection– reduction in the number of tickets, calls, or chats reaching human agents.
- Average resolution time– how quickly the agent solves common issues.
- Customer satisfaction– post-interaction surveys or ratings specific to virtual agent conversations.
- Agent productivity– improvements in the quality and speed of work handled by human agents, thanks to automation.
The Future of Virtual Agents
Virtual agents are evolving rapidly as AI and automation technologies mature. Several trends are shaping the future of these digital assistants.
- More natural conversations– advances in language models are enabling more fluid, context-aware interactions.
- Omnichannel experiences– users will be able to start a conversation on one channel and continue seamlessly on another, with full context preserved.
- Deeper personalization– virtual agents will leverage more data to tailor recommendations, actions, and tone to each individual.
- Stronger collaboration with humans– instead of replacing people, virtual agents will increasingly act as co-pilots, suggesting answers and automations to live agents in real time.
Organizations that adopt virtual agents thoughtfully today position themselves for a more agile, customer-centric future.
Frequently Asked Questions About Virtual Agents
Are virtual agents the same as AI chatbots?
Virtual agents are a type of AI chatbot, but they typically offer more advanced capabilities than simple rules-based bots. They focus on understanding user intent, managing multi-step conversations, and integrating with business systems to complete tasks, not just answer questions.
Do virtual agents replace human agents?
Virtual agents are designed toaugmenthuman teams, not replace them. They handle repetitive, low-complexity interactions so human agents can focus on more complex, sensitive, or relationship-driven work. The most successful organizations use a blended model where virtual and human agents collaborate.
Which channels can a virtual agent support?
Virtual agents commonly appear on websites, mobile apps, messaging platforms, and sometimes voice channels. Many solutions can be deployed across multiple channels, providing a consistent experience wherever users choose to engage.
How long does it take to see value from a virtual agent?
Timelines vary by scope and complexity, but many organizations start to see measurable benefits within a few months of launch. Quick wins often come from focusing on a handful of high-volume, predictable use cases that can be automated effectively.
Is a virtual agent right for small organizations?
Yes. While virtual agents are popular with large enterprises, smaller organizations can also benefit. Even modest levels of automation can free up staff, improve response times, and offer 24/7 support without significantly increasing costs.
A virtual agent is more than a trend; it is a practical, proven way to deliver faster, smarter, and more scalable support. By combining AI, automation, and thoughtful design, you can create a digital assistant that delights users, empowers your team, and moves your organization closer to a truly modern service experience.
